Category
Contact Form
Post Top Ad
Author Details
Recent Posts
January 07, 2020
December 25, 2019
February 22, 2017
6 gotta-know Spotify tips for Android and iOS
by Inam Ullah |
in IOS TUTORIALS
at 08:36
There’s more to the Spotify app for Android and iOS than
simply streaming your favorite artists or Spotify’s premixed radio
stations. Indeed, the Spotify mobile app is capable of some pretty
clever tricks once you know what you’re doing.
For starters, it’s easy to download a Spotify radio mix
to your phone for on-the-go playback without putting a dent in your
monthly mobile data allowance—and indeed, you can set Spotify to stay
offline completely, if the need arises. You can also tweak the quality
of your audio streaming and music downloads, keep playing tunes even
when your playlist is over, “crossfade” from one song to another, and
more.
Note: Several of the features and settings we’ll be
covering require a “premium” Spotify subscription, which will set you
back about $10 a month. (Psst! You can easily score a 30-day free Spotify Premium trial with the right Google search).
1. Play your radio stations offline
Whether
they’re based on a song, an artist, or a particular “mood,” Spotify’s
radio stations are perfect for playing endless tunes at home over Wi-Fi.
If you’re out and about, though, you might not relish the idea of
streaming all that music over cellular, or perhaps you’re on a subway,
soaring at cruising altitude, or otherwise unable to get a wireless
connection.
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
Luckily, there’s a simple way to save
Spotify radio stations for offline playback, perfect for bringing a
smorgasbord of tunes with you while you’re on the go.
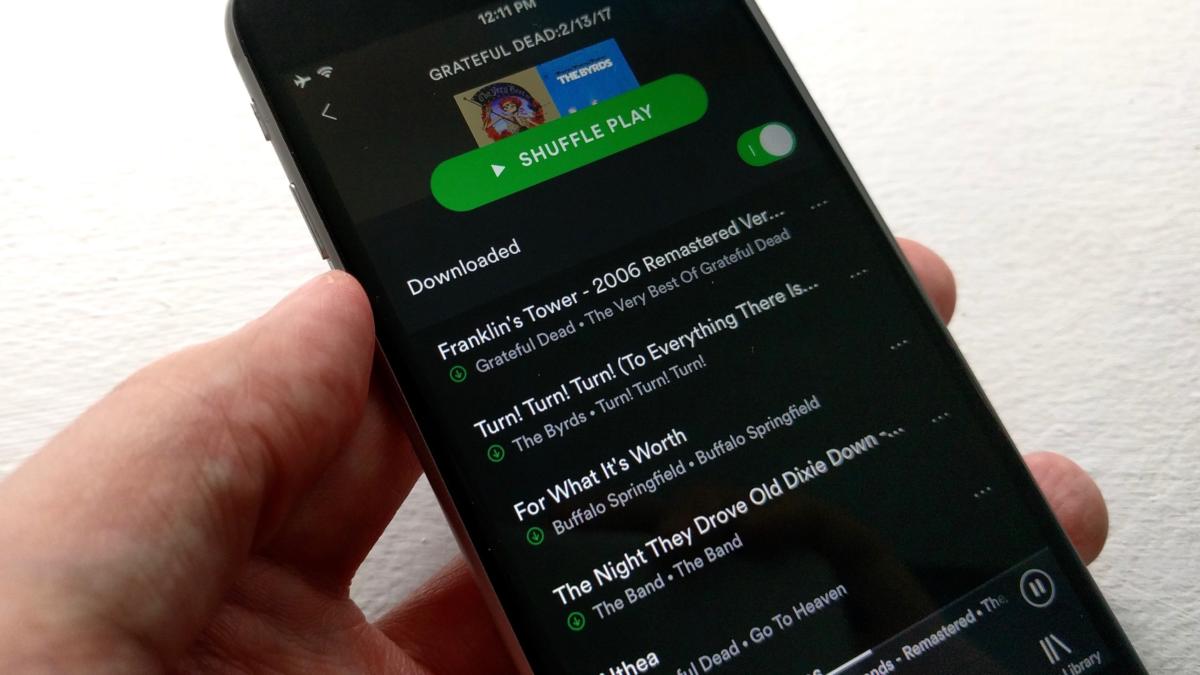
For iOS: This one’s easy. For a curated or “mood” station created by Spotify, just pull up the station, then flip on the Download switch.
For a custom station you’ve created (based on a song or
an artist), tap the three-dot button in the top-right corner of the
screen, then tap Add to Playlist. You can then add the tracks
in your radio station to an existing playlist or create a new one (the
default name for a new playlist will be the name of the station plus a
timestamp). Once that’s done, go to your new playlist (it’s under the Your Library tab), then flip on the Download switch.
For Android: For premade Spotify radio stations, the process is the same as iOS—just open a station, then switch on the Download setting.
For
your own radio stations, you’ll have to jump through a few hoops,
because (for whatever reason) the Android version of Spotify doesn’t
have a simple “Add to playlist” button for an entire station. Instead,
you’ll have to tap the three-dot button next to each song in the
station, then tap Add to playlist—tedious, I know.
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
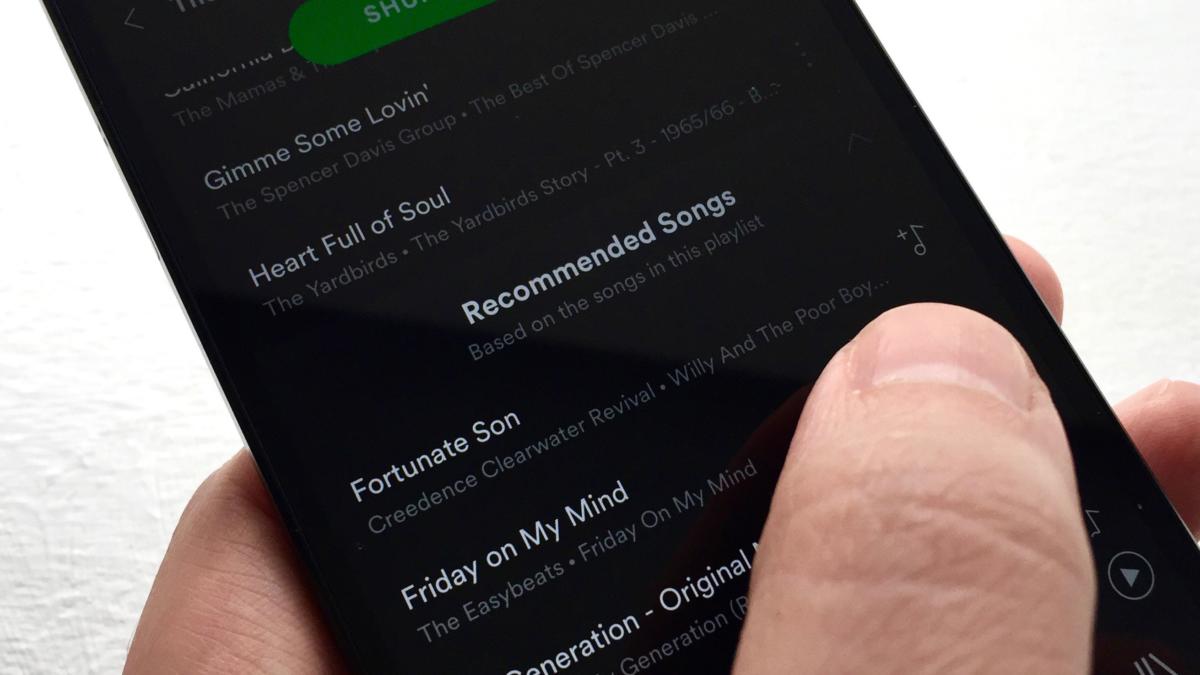
Another option: Add just a few songs to a new playlist, open the playlist (from the Your Library tab), then tap the “+” buttons next to the tracks in the Recommended Songs section.
Yet another option: Open your custom station
using the Spotify desktop app, click the three-dot button near the top
of the screen, then click Add to playlist. Once you’ve created a new playlist with tracks from your radio station, the playlist will appear in the Android app.
Finally got your radio playlist created? Open it up (Your Library > Playlists), then flick on the Download setting.
2. Listen to Spotify offline, and only offline
Once
you’ve got some radio stations saved for offline playback, you might
want to be sure that you don’t accidentally start streaming Spotify
tunes over your cellular connection, particularly given Spotify’s AutoPlay feature (which I’ll cover in a moment).
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
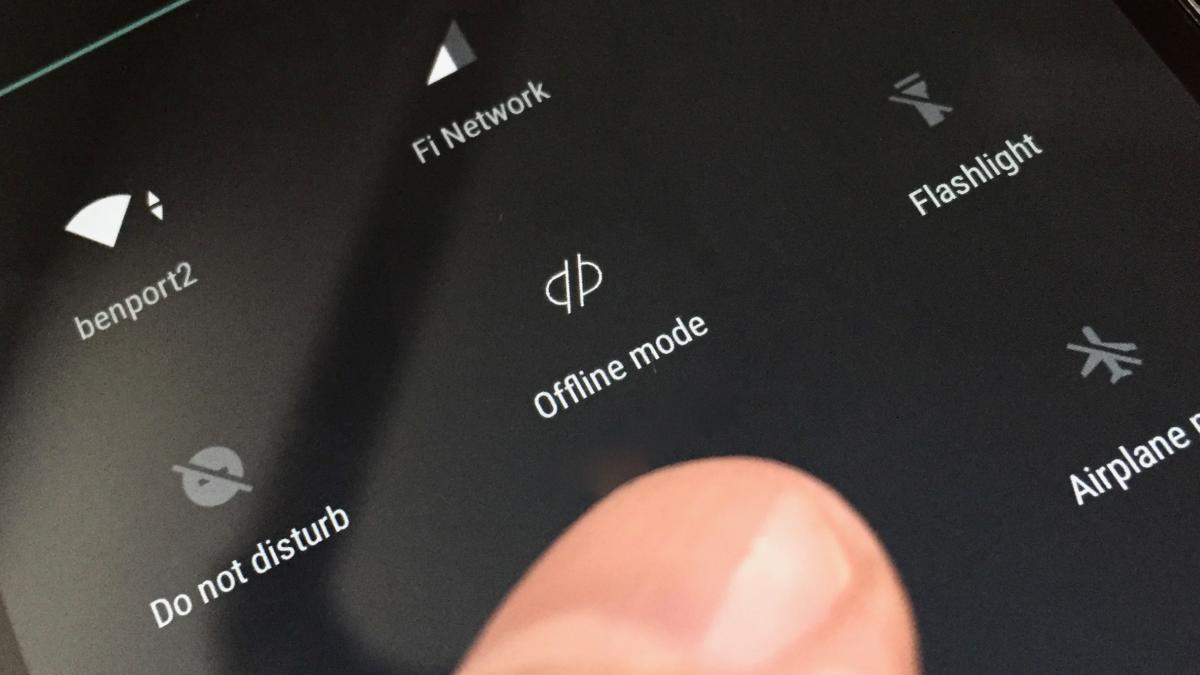
Here’s the trick: Turn on Spotify’s Offline mode, which will only let you play Spotify tracks and playlists that you’ve downloaded.
For Android, tap the Your Library tab at the bottom of the screen, tap the Settings button in the top-right corner of the screen, then flip the Offline mode switch. For iOS, head for the Your Library tab, tap Settings > Playback, then enable Offline mode.
If you’ve got Nougat installed on your Android phone,
you can add an Offline button for Spotify to your Quick Settings panel.
Open Quick Settings (swipe down with two fingertips from the top of the
screen), tap the Edit button at the top of the screen, then look for the Offline mode button in the Drag to add tiles section.
3. Keep playing music when your playlist runs out
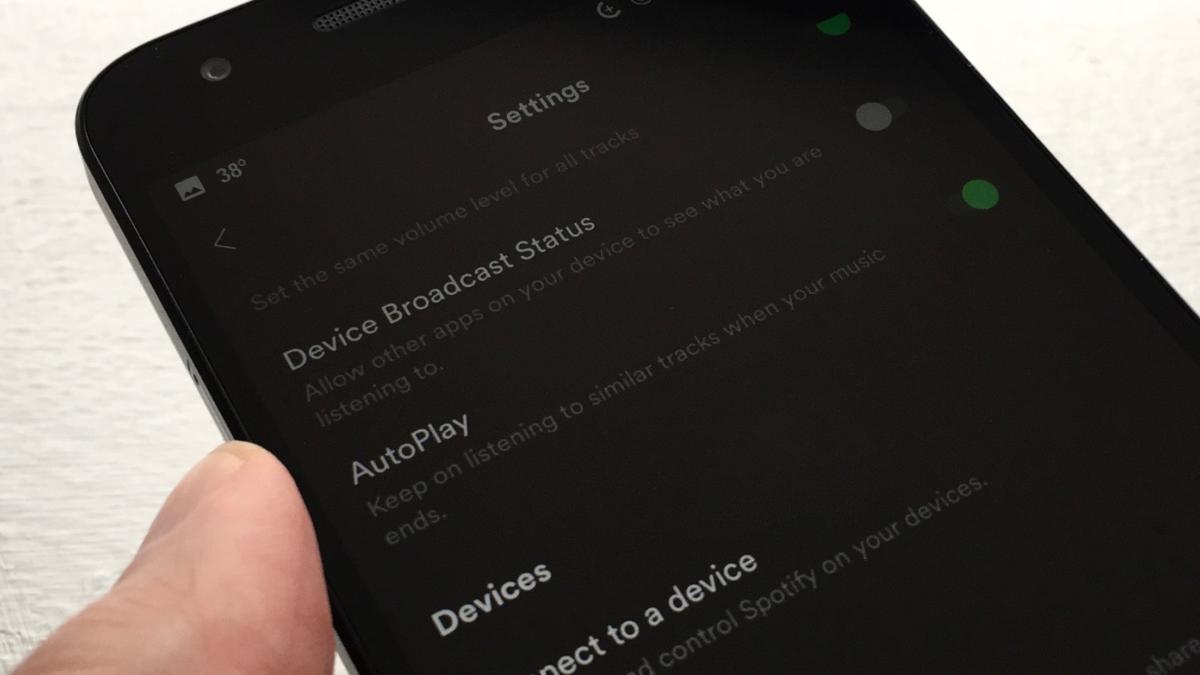
If you never want the music to end, Spotify has a clever feature just for you. The AutoPlay
setting (yes, the one we referred to above) will automatically play
“recommended” songs after the playlist or album you’re listening to
ends.
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
It’s a nifty feature for anyone who wants continuous tunes without looping the same tracks over and over—and yes, with AutoPlay enabled, you might end up streaming songs after your downloaded playlist tracks are done (unless, of course, you’ve turned on Offline mode).
On Android, tap Your Library > Settings, then toggle the AutoPlay setting on or off. On iOS, you’ll need to tap Your Library > Settings > Playback to reach the AutoPlay switch.
4. Snip out the gaps between songs
Nothing
ruins the mood of “Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band” (yes, I’m
dating myself) like a jarring skip between the title track and “With a
Little Help from My Friends.” Luckily, you can set Spotify to eliminate
the gaps between songs, which makes for a much more seamless Fab Four
experience.
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
On Android, tap Your Library > Settings, then toggle on the Gapless setting. For iOS, tap Playback from the Settings screen to reach the Gapless setting.
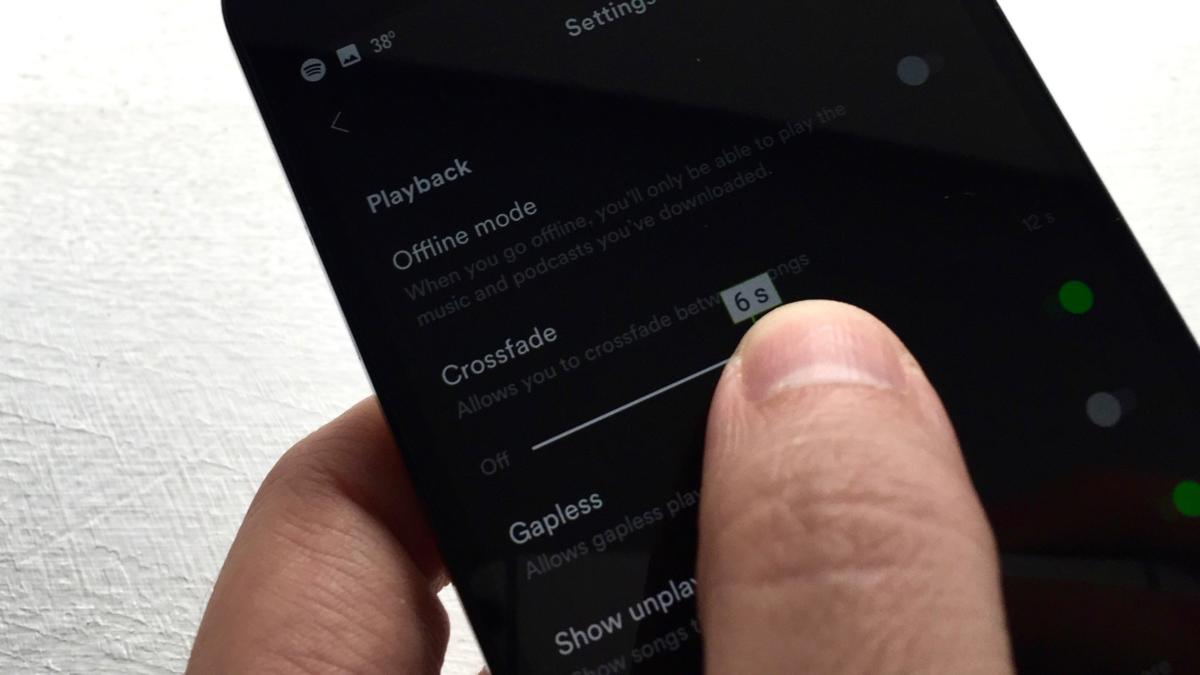
5. Crossfade between songs
Some albums, like Sgt. Pepper’s... were meant to be enjoyed without gaps between songs, but perhaps you’re a music lover who never wants silence between tracks, no matter what. If that’s the case, Spotify has a setting for you.
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
Head for Spotify’s Playback settings (Your Library > Settings on Android, or Your Library > Settings > Playback on iOS), then swipe the Crossfade slider for anywhere between one and 12 seconds of crossfade.
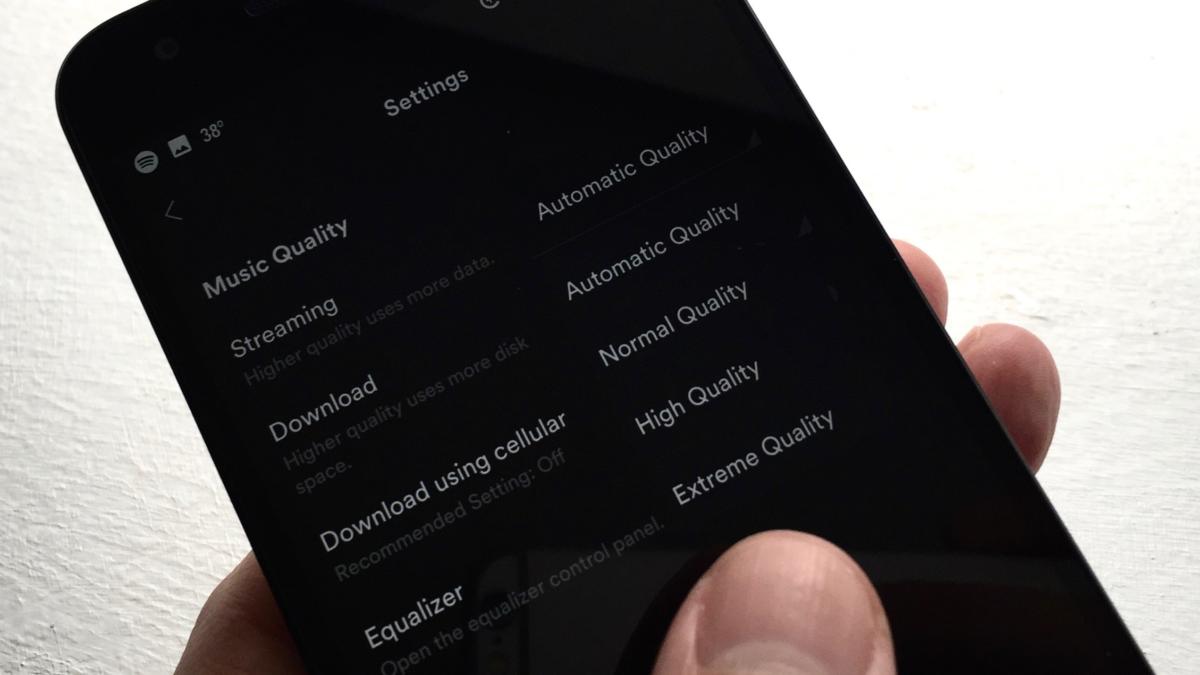
6. Boost your playback quality
By
default, Spotify will automatically adjust your music streaming
bandwidth depending on the strength of your wireless connection, while
downloaded tracks will be optimized for the best balance between sound
quality and storage space.
 Ben Patterson
Ben Patterson
Spotify’s Automatic and Normal
settings for streaming and downloads, respectively, should sound decent
enough for most casual listeners. If you’re ears demand the best,
there’s a way to wring every last bit out of Spotify’s music streams and
downloaded tracks.
First, tap your way to Spotify’s Streaming quality settings (Your Library > Settings on Android, or Your Library > Settings > Streaming quality on iOS), then pick some new options. For Streaming, you can choose from Automatic quality, Normal (about 96KBps, not bad for mobile), High (160KBps—better), or Extreme (320KBps, for silky-smooth sound). For Download quality, your choices are similar: Normal, High, and Extreme. Naturally, the better your streaming or download quality, the more bandwidth and storage you’ll consume.
Apple iOS Latest News: Third Beta 10.3 Now Relased to All Developers Bringing New Updates & Changes
by Inam Ullah |
in Technology
at 08:33
Apple has recently implanted its third beta of iOS 10.3 to all
developers. This beta comes with new features along with its new Theatre
Mode which was packed with other bug fixes and major improvements in
terms of stability.
Today, Apple launches its third beta of an upcoming iOS 10.3 update to all developers; two weeks after implanting the second beta of iOS 10.3. It's been two months since the last release of iOS 10.2 was done; the last major update to the iOS 10 Operating System, according to Mac Rumors.
Good news for all registered developers! You can now download the
third iOS 10.3 beta from the Apple Developer Center which is a major
update from the company. The third beta iOS 10.3 will feature new
updates and changes to the iOS 10 operating system such as Find My
Airpods which was designed to help Apple Airpod users to locate a lost
earphone. Find My Airpods will record its last known location of when
and where Airpod was last connected via Bluetooth to an iOS device, and
it can still play a sound on a lost Airpod.
The latest update of Apple will also bring a new Apple File System (APFS), it will automatically be installed on every iOS device that is updated to iOS 10.3. It will also amend for flash/SSD storage along with a strong encryption.
The Apple Company also plans to bring some minor App Store changes in iOS 10.3 which will allow developers to react to customer reviews for the first time. iOS consumers are now able to put some commendations for reviews in the App Store by marking it as Helpful or Not Helpful, as claimed by the reports of Todays iPhone. But for the record, Apple also put limits on the number of reviews by the developers that provide a Master Switch which let users turn off all app review requests.
Apple also redesigned the app open/close animation, a better breakdown of iCloud storage usage, an Apple ID profile Settings and developments to SiriKit. For the App Compatibility, visit the Setting app, a new App Compatibility section; it can be accessed by opening the Settings app and clicking the General.
Today, Apple launches its third beta of an upcoming iOS 10.3 update to all developers; two weeks after implanting the second beta of iOS 10.3. It's been two months since the last release of iOS 10.2 was done; the last major update to the iOS 10 Operating System, according to Mac Rumors.
The latest update of Apple will also bring a new Apple File System (APFS), it will automatically be installed on every iOS device that is updated to iOS 10.3. It will also amend for flash/SSD storage along with a strong encryption.
The Apple Company also plans to bring some minor App Store changes in iOS 10.3 which will allow developers to react to customer reviews for the first time. iOS consumers are now able to put some commendations for reviews in the App Store by marking it as Helpful or Not Helpful, as claimed by the reports of Todays iPhone. But for the record, Apple also put limits on the number of reviews by the developers that provide a Master Switch which let users turn off all app review requests.
Apple also redesigned the app open/close animation, a better breakdown of iCloud storage usage, an Apple ID profile Settings and developments to SiriKit. For the App Compatibility, visit the Setting app, a new App Compatibility section; it can be accessed by opening the Settings app and clicking the General.
Create a Bootable USB Flash Drive
by Inam Ullah |
in PC Tutorials
at 08:26
You can create a bootable USB flash drive to use to deploy Windows Server 2012 Essentials . The first step is to prepare the USB flash drive by using DiskPart, which is a command-line utility. For information about DiskPart, see DiskPart Command-Line Options.
For additional scenarios in which you may want to create or use a bootable USB flash drive, see the following topics:
- Restore a full system from an existing client computer backup
- Restore or repair your server running Windows Server Essentials
To create a bootable USB flash drive
- Insert a USB flash drive into a running computer.
- Open a Command Prompt window as an administrator.
- Type
diskpart. - In the new command line window that opens, to determine the USB flash drive number or drive letter, at the command prompt, type
list disk, and then click ENTER. Thelist diskcommand displays all the disks on the computer. Note the drive number or drive letter of the USB flash drive. - At the command prompt, type
select disk <X>, where X is the drive number or drive letter of the USB flash drive, and then click ENTER. - Type
clean, and the click ENTER. This command deletes all data from the USB flash drive. - To create a new primary partition on the USB flash drive, type
create part pri, and then click ENTER. - To select the partition that you just created, type
select part 1, and then click ENTER. - To format the partition, type
format fs=ntfs quick, and then click ENTER.
 Important
Important If your server platform supports Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), you should format the USB flash drive as FAT32 rather than as NTFS. To format the partition as FAT32, type format fs=fat32 quick, and then click ENTER. - Type
active, and then click ENTER. - Type
exit, and then click ENTER. - When you finish preparing your custom image, save it to the root of the USB flash drive.
How To Activate Windows 10 Pro/Home/Enterprise using KMSpico 10 Activator
by Inam Ullah |
in PC Tutorials
at 08:26
Tutorial - How To Activate Windows 10 Pro/Home/Enterprise using KMSpico
10 Activator. Now You can activated all edition of Windows 10 for free
it working with 32 Bit and 64 Bit operating system. You can also check
out How To Download Windows 10 ISO image on your PC.
Windows 10 Activation Pre-Requirement
- KMSpico Activator (Download from Below)
- Turn off Windows Defender/ Antivirus Software
How To Activate Windows 10
Step 1. Download KMSpico software from below Link.
Step 2. Turn off your antivirus/Windows Defender until windows get activated (select turn off permanently then turn on).
Step 3. Extract downloaded file on your PC
Step 4. Just run KMSAuto Net as Administrator.
Step 5. Click on Activation Button and wait until its finished.

How to start Android app development for complete beginners in 5 steps
by Inam Ullah |
in Android Hacks
at 08:24
 So
you have a killer app idea and you’re ready to turn it into a reality
and take it to market. No doubt you’re itching to start getting your
first downloads, reviews and profits… But there’s just one problem: you
don’t have a clue where to start!
So
you have a killer app idea and you’re ready to turn it into a reality
and take it to market. No doubt you’re itching to start getting your
first downloads, reviews and profits… But there’s just one problem: you
don’t have a clue where to start!
Learning to code is difficult enough on its own but with Android
development it can be more complicated. Not only do you need to
understand Java, you also need to install all the Android-specific
software and learn all of the unique quirks of Android app development.
In general, creating an Android app requires the SDK (Software
Development Kit), an IDE (Integrated Development Environment) like Android Studio or Eclipse,
the Java Software Development Kit (JDK) and a virtual device to test
on. All this takes work to set up, and that’s before you’ve even started
looking into things like Google Play Services, screen sizes, API
levels…
See also:
I want to develop Android Apps – What languages should I learn?
July 29, 2016
It’s just such a dense amount of information and it’s enough to
put an awful lot of people off before they even begin. My aim with this
article then, is to provide an approachable guide to try and make the
whole prospect of creating an app a little less daunting… I’ll explain
the bits you need to know and gloss over the rest and by the end you
should have a basic app that you can start iterating on and
experimenting with.
Go and make yourself a cup of tea first though, this may take a while…
Step 1: Download Android Studio
To program in most languages, you need a piece of software called
an IDE or ‘Integrated Development Environment’. The most common IDE for
Android development is Android Studio, which comes direct from Google itself. You can get it here.
An IDE is what gives you the main UI where you’ll enter your code
(you can’t just start typing into notepad). It also highlights things
you get wrong, offers suggestions and lets you run and test your
creations conveniently. It creates the files you need, it provides basic
layouts and generally it saves you a lot of time and effort.
What’s great about Android Studio is that it is designed
specifically for Android development (unlike the second most popular
option, Eclipse). This means that when you download the software, you’ll
also get a lot of the other bits you need including the Android SDK (a selection of tools including the Android platform itself) and the Android Virtual Device,
which is an emulator you can test your apps on. When you go through the
installation, make sure you leave the boxes ticked to confirm that you
want these additional components. You could manually add them later, but
this will just complicate matters.
As mentioned, there are some alternatives to Android Studio. Eclipse
is an older IDE that can be used for developing other things too (such
as iOS apps) and that is a bit more flexible overall. It’s also a much
more fiddly to get started with though and not nearly as
beginner-friendly. Another personal favorite of mine is Basic4Android.
Basic4Android is an IDE that lets you code Android apps with the BASIC
programming language. It makes things easier in a number of other ways
too and is focused on ‘rapid development’.
See also:
Writing your first Android game using the Corona SDK
July 13, 2015
There are other options too, such as Unity3D and numerous app
builders, each of which has specific strengths and weaknesses depending
on what you’re planning on building. For the sake of simplicity though,
we’re focusing on Android Studio because it has become the ‘main’ way to
build basic apps and pretty much the industry standard. If you think
you might ever sell your business, if you want to give yourself the most
flexibility and control possible, or if you’d like to become a
professional app developer, you’ll need this tool.
That said, if you read through all this and you find it too much
still, you might want to consider Basic4Android as a simpler approach
and I’ll be covering that in a future post.
Okay, just to recap: we now have Android Studio downloaded and
installed. But, don’t run it until you read step two! So far so good…
What could possibly go wrong?
Step 2: Setting Up Android Studio
Now you have Android Studio installed you’ve taken your first,
bold step toward becoming a developer! A lot of people only manage it
this far and then leave the software installed on their computer for
months on end, feeling guilty every time they see it in the Start Menu.
Eventually they end deleting it to make space for the next AAA title on
Steam and so ends the whole sorry affair… Don’t end up like them – it’s
time for some more affirmative action!
Before you can get started, you also need to install Java on your
machine to use Android Studio. Specifically, you’re going to need
install the Java Development Kit (JDK). Java is the programming language
you’re going to be using to build your apps in this instance and you
need to install the JDK in order for Android Studio to be able to
interpret and compile your code (compiling means turning the source into
something that is understood by the CPU – machine code). You’ll find
the Java Development Kit here. Just download and follow the instructions to install.
See also:
Android Studio tutorial for beginners
September 1, 2015
Now you can click on Android Studio to launch it. Once
it opens up, you’ll be presented with a menu where you’ll be able to get
started or configure some options. The great thing is that everything
is handled for you at this point, though you may want to familiarize
yourself with the SDK Manager (Configure > SDK
Manager) which is where you’ll update your Android SDK to support newer
versions, as well as download things like code samples or support for
Google Glass. But don’t worry about that now but if Android Studio says
you’re missing something, this is where you’ll probably need to go to
find it.
So really there are three main things interacting when you use Android Studio to create your apps.
- Android Studio itself, which is an IDE that provides you with a nice interface for coding.
- The code you write in Java, which you installed a moment ago…
- And the Android SDK which you’ll access through your Java code in order to do Android-type things
If you find this all a bit complicated and daunting then… well, you don’t know you’re born. This used to be way worse.
Maybe that offers some consolation…
Step 3: Starting a New Project
Once you’ve installed your samples, you can go back to the first
page you saw when you loaded up Android Studio. Now you want to choose Start a new Android Studio Project – it’s finally happening!
Enter the name you want for your application and your ‘company
domain’. Together these elements will be used to create your package
name with the following format:
com.companyname.appname
The package will be the compiled file or APK (‘Android
Package File’) that you’ll eventually upload to the Google Play Store.
There are ways that people can see this, so if you’re planning on making
something you’ll eventually release, try to stay away from using ‘funny
words’.
The last field to enter is the directory where you want to save
all the files pertaining to your app. I like to save in DropBox to make
sure I always have a backup of my code. Click Next again and guess what…
More options! Huzzah! Don’t worry, we’re nearly there…
Next you need to decide what type of device you’re going to be developing for and in this case we’ll start with the Phone and Tablet
option. Other options are TV, Wear and Glass. It’s fine if you want to
develop for a myriad of platforms in the future – that’s one of the
wonders of Android – but let’s start with something a bit more
straightforward to begin with, okay?
The other choice you have to make at this stage is the ‘Minimum
SDK’. This is the lowest version of Android you want to support. Why not
just enter the latest version of Android in here? Well, because
relatively few people actually have the latest version of
Android installed on their device at any given time. You want to support
phones that are still running older versions in order to reach the
largest possible audience – especially overseas.
Why not just go with Android 1.1? Well, apart from this not being
an option (Froyo is as low as you can go), that would also prevent you
from using any of the fancy new features from the latest updates.
The best bet at this stage is to go with the default option, so
just leave this field as it is. On the next page, you’ll be given the
option to pick the way you want your app to look at the start. This will
be the look of your main ‘Activity Module’ which is
basically the main page of your app. Think of these like templates; do
you want to have the title of your app along the top of the screen, or
do you want your UI to fill the whole display? Do you want to start off
with some elements ready-designed for you? Is your app primarily going
to use Google Maps (don’t go here for a bit, things get more complicated
with Google Play Services).

Bear in mind that an app can have multiple activities that act
like separate pages on a website. You might have a ‘settings’ activity
for instance and a ‘main’ activity. So the activity isn’t the app per say but rather one stand-alone page of your app.
For your first creation though, you’ll probably do best to make something really simple that just displays a single, basic activity. Select ‘Basic Activity’
to keep things as simple as possible and for all intents and purposes,
this will now be your app. Click Next again you get the last few
options.
Now you get to pick the name for your activity and the layout
name (if you chose ‘Basic Activity’ you’ll also have the title option
and the ‘menu_resource’ name). The activity name is how you’ll refer to
your activities in your code, so call it something logical (good advice
for coding generally) like ‘MainActivity’. Creative, I know.
The layout name meanwhile describes a file that determines the
layout of an activity. This is a separate piece of code that runs in
concert with the main activity code to define where elements like images
and menus go and what fonts you’ll use. This is actually not Java but
XML – or Extensible Markup Language if you want to impress your friends.
For anyone with a background in web development, your XML is
going to work a little like HTML or a CSS style sheet. The Java code for
the activity meanwhile says what the elements on the screen do
when pressed etc. It’s fine to leave the default name here as
‘activity_main’. Lastly, choose a name for the menu and for the title.
Pick something nice for the title, as your users will be able to see
this at some points. Click next… and now you get to see your app!
Your blank, useless app… All that just to get started! You see
why people give up? But really we can break it down into the following
very basic steps:
- Download and install Android Studio, making sure to include the Android SDK
- Install Java SDK
- Start a new project and select the basic details
So it’s really not that bad… And remember: once you’ve done all
this once, you can forget about it forever and focus on the fun stuff:
creating apps! Your tea is probably cold at this point, so the next very
important step, is to get more.
Step 4: Making an Actual Thing
Once your app opens, you should see a directory tree on the left
with all the different files and folders that make up your app and a
picture of a phone displaying ‘Hello World!’ in the center. Well, hello
to you as well!
(A basic app that displays ‘Hello World’ is what most new
developers make first when they learn to program in a new language.
Android Studio cheats though, because it does it for you!)
You might notice that the open tab (along the top) is
‘activity_main.xml’, which is what the big phone is showing on its
display. You may recall that activity_main.xml is the XML code that
defines the layout instructions for your main activity.
If you selected ‘Basic Activity’ when you started your project,
then you’ll see a second XML file too called ‘content_main.xml’. For the
most part, these two do the same thing but the ‘acitvity_main.xml’
contains the basic layout that Android Studio created for you when you
selected ‘Basic Activity’. The stuff you want to edit is in
content_main.xml, so open that up and don’t worry about it for now.
(If this isn’t what is open to start, then use the directory on the left to open it by choosing: app > res > content_main.xml.)
The Layout
Android Studio is not showing the XML code itself here but rather
a rendering of how the layout will appear on the screen. This is a
visual editor a bit like Dreamweaver for web design and it makes life a
little easier for us developers.
You also have a bunch of options called ‘widgets’
down the left that you can add to your app. This is your basic app
stuff; so for instance, if you want to add a button saying ‘OK’ to your
activity, you can simply drag it over to the screen and drop it anywhere
you like. Go ahead and dump an ‘OK’ button right underneath the ‘Hello
World’.
Something else you’ll find is that you can click on either of
these elements in order to change the text and the ‘ID’. The ID is how
you’re refer to each element (called a ‘view’) in your Java code, while the text is of course what you display to the user.
Delete the ‘Hello World’ widget (or view) and change the text on
the button to ‘Hello?’. Likewise, change the ‘id’ on the button to
‘button1’.
I am now stealthily getting you to write a little program… Notice
as well that when you select a view, you get options in the bottom
right to change the text color and size etc. You can play around with
these variables if you like to change the look of your button. We’re
coming back here in a minute though so make a mental note!
See also:
Java tutorial for beginners
March 14, 2016
Now open up your MainActivity.java. The tab will be along the top but in case it isn’t, find it under: App > Java.
This is the code that defines the behavior of your app. At this stage, you’re going to add in a little passage of code:
javaSelect All
javaSelect All
public void buttonOnClick(View v) {
Button button1 = (Button) v;
((Button) v).setText("Hello!");
}
This is going to go right underneath the first lone closed bracket ‘}’, just before the “@Override, Public Boolean”. It should look like this:
What does it all mean? Well basically, anything following “void buttonOnClick” will be carried out when someone clicks on the button. We’re then finding the button with the “Button button1 = (Button) v;” code and then changing the text.
Yes, there are other ways you could achieve the same thing but I
feel like this keeps it nice and simple and thus easy to understand.
Spend some time reading it and try to get your head around what is doing
what…
At the top of the page is the word ‘import…’. Click on that to expand it and make sure that somewhere there is the line: “import android.widget.Button;”.
It should have appeared on its own when you typed out the last bit
(Android Studio is smart like that) but you can add it yourself if it
didn’t.
(Notice as we type that lines end in “;”. This is basic Java
formatting and if you forget one, it will throw up an error. Get used to
searching around for them!)
Now go back to your content_main.xml and click on the button. In
the right corner, where you have your parameters for the button, you
should be able to find an option called ‘onClick’. Click on this and
then select the ‘onClick’ line of code you just wrote from the drop down
menu. What you’ve just done, is told Android Studio that you want to
associate the section of code with the button you created (because
you’ll have lots of buttons in future).
Now all that’s left to do is run the app you just made. Simple go
to ‘run’ along the top and then select ‘run app’ from the drop down
menu. You should already have your AVD (Android Virtual Device)
installed but if not, you can go to: tools > Android > AVD Manager > + Create Virtual Device. Don’t forget you also need to install an Android version onto the device.
 Follow the steps to launch the emulator running your app. Be patient, it can sometimes take an age to load up… If it never loads
up, you can consider ‘packaging’ the app in order to create an APK.
Drag this onto your Android device and double click on it to install and
run it.
Follow the steps to launch the emulator running your app. Be patient, it can sometimes take an age to load up… If it never loads
up, you can consider ‘packaging’ the app in order to create an APK.
Drag this onto your Android device and double click on it to install and
run it.
Once it’s finally up and running you can have a go with this fun,
fun app. What you should find is that when you click the button, the
text from ‘Hello?’ to ‘Hello!’. We’re going to be rich…
(If it doesn’t work… something has gone wrong. It wasn’t me, my
one works! Look for red text in your code and hover your mouse over it
to get suggestions from Android Studio.)
Step 5: How to Get Better At App Development
Okay, so that was a lie. We’re probably not going to be
rich. At the moment the app we’ve made is pretty lame. You can try and
sell it sure but you probably won’t get that many good reviews.
The reason I talked you through this basic app creation though is
because it teaches you the very fundamentals of programming. You have
an action and a reaction – pressing on a button does something.
Throw in some variables and some math, add some pretty images and a
useful function and that’s genuinely enough to make a very basic app.
So where do we go from here? There’s so much more to learn: we haven’t looked at the Android Manifest yet, we haven’t talked about your private keysign (or how fun it is when you lose that) and we haven’t even studied the Android app ‘lifecycle’ (nothing to do with The Lion King). There’s issues with supporting different screen sizes and there’s just so much more to learn.
Unfortunately, it would take an entire book to teach you the entirety of Android app development. So that’s a good place to start: buy a book!
But more important is just to play around and try things. Don’t
set out to make your world-changing app on day one. Instead, focus on
making something simple and straightforward and then build on that. Try
changing the layout of the text and try adding in more buttons and more
rules to make your app actually useful.
Eventually, you’ll find there’s something you want to do that you
can’t figure out on your own. Maybe you want a sound to play when
someone clicks on your button, for example. This is where the real
learning starts. Now all you need to do is search in Google: “How to
play sound onClick Android”
You’ll find a bunch of complicated answers but eventually someone, probably on Stack Overflow,
will break down the answer simply for you. Then what you do is you copy
that code and you paste it into your app, making a few changes as you
go.
Likewise, try out some of the code samples available through
Android studio. See how they work, try changing things and just
experiment. Things will go wrong and error messages will come up but for
the most part, if you just follow the instructions, it’s easy enough to
handle. Don’t panic! And that’s pretty much how you learn to make apps.
A lot of it boils down to reverse engineering and copying and pasting.
Once you have the main program in place, the rest you pick up as you go.
If you want the absolute easiest way to start, then just find
some sample code that’s close to what you make and change it. No one is
going to be able to explain all this to you in a way that makes any
sense and if you worry about not grasping everything to begin with,
you’ll never get anywhere.
So instead, dive in, get your hands dirty and learn on the job. It’s complicated and it’s frustrating but ultimately it’s highly rewarding and more than worth the initial effort.
Popular Posts
Labels
STAY WITH US
Contributors
About Us
Proudly Powered by Blogger.